Wireless Standards for Smart Buildings: Enhancing Efficiency, Security, and Scalability
August 6th 2024Wireless Standards for Smart Buildings: Enhancing Efficiency, Security, and Scalability
Thanks to incredible technological advancements, smart buildings have become the norm. Wireless technology helps make these innovative structures a reality, enabling different systems to work together seamlessly.
However, this technology requires specific standards.
Wireless standards ensure that everything from lighting and HVAC to security and energy management can communicate and function efficiently.
We rely increasingly on wireless standards for transmitting data and integrating systems. These standards set the rules for how devices and systems talk to each other, allowing for real-time monitoring, control, and automation.
These standards are necessary to ensure that devices from different manufacturers can work together smoothly, leading to inefficiencies and potential problems.
Our valued partner, EnOcean, has published an insightful article on wireless standards for smart buildings. Below, we’ll summarize the article, discuss various wireless protocols available, and provide a detailed comparison to help you choose the best one for your project.
Understanding Wireless Standards for Smart Buildings
Wireless standards are protocols that define how devices communicate with each other without the need for physical connections. In smart buildings, these standards are crucial for ensuring that various systems and devices can work together seamlessly. They set the guidelines for data transmission, signal strength, and communication protocols, which are essential for the smooth operation of smart building technologies.
The importance of wireless standards in smart buildings cannot be overstated. These standards ensure compatibility and interoperability between devices from different manufacturers.
Without standardized protocols, integrating multiple systems—such as lighting, HVAC, security, and energy management—would be a complex and often unreliable process. Wireless standards provide a common language for these devices, allowing them to exchange information and function cohesively.
Wireless standards also play a vital role in enabling efficient data transmission, control, and automation. They facilitate real-time communication between devices, allowing for immediate response to changes in the environment or user commands.
This efficiency is vital to achieving the automation goals of smart buildings, such as optimizing energy use, enhancing security, and improving occupant comfort.
Choosing the proper wireless standard is a critical decision that can significantly impact the efficiency, security, and scalability of your smart building system. The challenge lies in navigating through the various options and understanding the nuances of each standard.
Many factors play a vital role in this decision-making process, such as:
- Compatibility
- Data transmission rates
- Range
- Power consumption
- Security
To make an informed decision, it's important to have a well-defined list of criteria. These criteria will help you systematically evaluate each wireless standard and determine which aligns best with your project's goals.
Proposed Criteria For Wireless Standards
When evaluating wireless standards for smart building systems, a comprehensive set of criteria must be used to ensure the chosen protocol meets the specific needs and requirements of the building's infrastructure and applications.
Here are the proposed criteria inspired by EnOcean's framework:
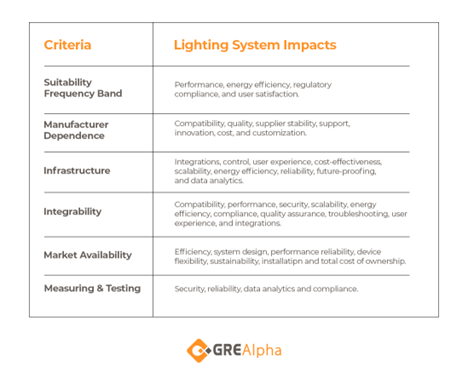
- Suitability of the frequency band (KO Criterion) - Assess whether the frequency band is appropriate for the building's environment and applications. The frequency band must support reliable communication within the building's structure and layout, avoiding interference with other wireless systems. This is a knockout criterion, meaning the standard should be eliminated from consideration if the frequency band is not suitable.
- Manufacturer dependence - Evaluate the extent of reliance on specific manufacturers for components and support. Multiple manufacturers should ideally support a wireless standard to ensure a competitive market, availability of parts, and long-term support. High dependence on a single manufacturer can lead to issues with compatibility, supply chain disruptions, and higher costs.
- Infrastructure - Consider the infrastructure requirements for implementing the wireless standard. This includes the need for gateways, repeaters, and other network components. A standard with minimal infrastructure requirements can reduce complexity and installation costs while providing deployment flexibility.
- Integrability - Examine the ease of integrating the wireless standard with existing building systems. The chosen standard should support seamless integration with current and future systems, ensuring interoperability and reducing the need for extensive modifications or custom solutions.
- Market Availability - Check the availability of compatible devices and components in the market. A widely adopted standard with a broad range of available products ensures that components are readily accessible and competitively priced. This availability indicates industry support and the likelihood of ongoing development and innovation.
- Measuring & Testing - Assess the tools and methods available for measuring and testing the wireless standard. Effective measurement and testing capabilities are essential for ensuring the system's performance, diagnosing issues, and maintaining the network. The availability of user-friendly tools and comprehensive documentation is a significant advantage.
- Power Supply - Evaluate the power supply options, including self-powered, battery-powered, and mains-powered devices. The choice of power supply impacts the system's maintenance requirements, operational costs, and environmental footprint. Self-powered or energy-harvesting devices, such as those using EnOcean technology, offer significant benefits in reducing maintenance and improving sustainability.
- Data encryption - Consider the level of data encryption and security offered by the wireless standard. Robust encryption and security protocols are essential to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of the smart building system. Evaluate the standard's support for high-level data security measures to safeguard against potential threats.
- Overall assessment - Provide a comprehensive evaluation of the wireless standard based on the above criteria. This overall assessment should weigh each standard's strengths and weaknesses, considering the project's specific needs. By systematically evaluating these criteria, building managers and engineers can make informed decisions, leading to a more efficient, secure, and scalable implementation of smart building technologies.
Why These Standards Are Important for Automation and Control
Wireless standards are crucial for the automation and control systems of smart buildings. They provide the framework for devices and systems to communicate, enabling real-time monitoring, control, and automation.
Caption: Choosing the right wireless standard enhances efficiency, security, and scalability. The appropriate standard ensures reliable data transmission, reduces latency, and minimizes interference, leading to more responsive operations.
Enhanced security protocols protect data and prevent unauthorized access, maintaining system integrity. Scalability allows the system to grow and adapt without significant overhauls.
Implementing wireless standards can lead to various benefits, such as reduced maintenance costs with energy-harvesting technology, seamless integration of systems like lighting, HVAC, and security, and improved energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
These advantages demonstrate how the proper wireless standard can lead to more efficient, secure, and adaptable smart building solutions.
Wireless Standards Are Crucial for Efficient Smart Buildings
At GRE Alpha, we recognize the crucial element of power supply choice in wireless standards. Different projects may benefit from different power solutions, and it's essential to consider these options carefully. Integrated lighting systems are part of the equation.
Many of today’s modern wireless LED drivers use robust wireless protocols, including:
Wireless standards offer a variety of power supply options. For instance, EnOcean's energy harvesting technology provides self-powered solutions that significantly reduce maintenance costs and enhance sustainability. On the other hand, battery-operated devices using BLE or Z-Wave protocols offer flexibility and ease of installation, though they may require periodic maintenance and battery replacement.
Choosing the right power source is vital for ensuring the longevity, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact of your smart building system. A well-chosen power supply can minimize operational disruptions, reduce long-term costs, and contribute to sustainable building practices. The GRE Alpha catalog offers various controllers to match project requirements.
By evaluating all the criteria and considering the specific needs of your project, you can make well-informed decisions that lead to more efficient, secure, and scalable smart building implementations.
Read the full article on wireless standards from EnOcean here.
Learn more about our EnOcean Wireless dimming Module here.
10 Smart Building Questions Asked By Lighting Designers
July 31st 202410 Smart Building Questions Asked By Lighting Designers
As smart home technology continues to evolve, lighting designers are increasingly focusing on the many benefits and considerations associated with integrating smart lighting systems.
Our valued partner, EnOcean Alliance, published a well-received whitepaper highlighting this attention in smart home technology.
Titled "Smart Buildings: IoT Solutions for Smart, Energy-Efficient Buildings," the piece emphasizes the transformative potential of smart buildings in enhancing energy efficiency, comfort, and operational performance through the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
It explores eight key considerations for end users and stakeholders, setting the stage for a deeper understanding of smart lighting systems:
- What is a Smart Building?
- What is the Market for Smart Buildings?
- How Does a Smart Building Work?
- What Are the Benefits of Smart Buildings?
- What Are the Benefits of Wireless Technology in Smart Buildings?
- Sustainability as a Mega Topic
- Focus on Existing and New Buildings
- A Dynamic Network for Professional Smart Buildings
Keeping with the spirit of EnOcean’s whitepaper, let’s look at 10 smart building and IoT lighting questions we often see asked by lighting designers.
How can smart lighting systems enhance operational efficiency and reduce energy costs?
Smart lighting systems optimize energy usage and streamline operations through advanced technologies like sensors and automated controls. These systems adjust lighting based on occupancy and ambient light, ensuring lights are used only when needed, significantly reducing energy consumption.
They also offer precise control over lighting intensity and schedules, cutting down on unnecessary energy use and extending the lifespan of fixtures. Integration with building management systems (BMS) allows for centralized control and real-time monitoring, helping facility managers identify inefficiencies and track energy usage patterns.
What standards and protocols are used for smart building integration?
Ensuring compatibility with established standards and protocols is crucial for seamlessly integrating smart lighting systems with other building systems. Key standards include:
- DALI (Digital Addressable Lighting Interface) - Standardized protocol for digital communication between lighting devices, allowing for precise control and flexibility in lighting systems.
- Zigbee - Wireless communication protocol widely used for home automation and smart lighting. It enables devices to communicate with each other through a mesh network, providing reliability and scalability.
- BACnet (Building Automation and Control Network) - Communication protocol for building automation and control networks, facilitating interoperability among different systems such as lighting, HVAC, and security.
How will the smart lighting system improve safety and security in the industrial environment?
Smart lighting systems significantly enhance safety and security in industrial environments through several advanced features:
- Emergency lighting - Smart lighting systems can automatically activate emergency lighting during power outages or emergencies, ensuring that critical areas remain illuminated.
- Motion detection - Integrated motion sensors can detect movement in unauthorized areas or during off-hours. Upon detecting motion, the system can increase lighting levels, trigger alarms, and alert security personnel.
- Real-time monitoring - Continuous real-time monitoring of lighting conditions allows immediate detection and response to irregularities or potential hazards. For example, if a light fixture fails in a critical area, the system can promptly alert maintenance staff to address the issue, ensuring consistent and reliable illumination.
- Enhanced visibility - Smart lighting systems can be programmed to adjust brightness and color temperatures to enhance visibility in specific areas, such as workstations or storage areas.
- Automated alerts and notifications - The system can be configured to send automated alerts and notifications to facility managers or security teams in case of lighting failures, unusual activities, or emergencies.
What types of sensors and controls are available for industrial applications?
In industrial applications, robust and reliable sensors and controls are essential for optimal performance and safety. Here are some key types of sensors and controls commonly used:
- Occupancy sensors - These sensors detect the presence or absence of people in a specific area. They can automatically turn lights on when a space is occupied and off when it's vacant, enhancing energy efficiency and security.
- Daylight sensors - Also known as photocells, these sensors measure the amount of natural light in a space and adjust artificial lighting accordingly. This helps maintain consistent lighting levels and reduce energy consumption by dimming or turning off lights when sufficient daylight is available.
- Temperature sensors - In harsh industrial environments, temperature sensors monitor ambient and equipment temperatures to prevent overheating and ensure optimal operating conditions. If temperatures exceed safe thresholds, these sensors can trigger cooling systems or alarms.
- Humidity sensors - These sensors measure moisture levels in the air, which is crucial for environments where humidity can affect machinery performance or product quality. They help maintain the appropriate humidity levels to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Vibration sensors - These are used to monitor the condition of machinery and equipment, and vibration sensors detect irregular vibrations that may indicate potential mechanical failures. Early detection allows for preventive maintenance, reducing downtime and repair costs.
- Air quality sensors - These sensors monitor the levels of pollutants and particulates in the air, ensuring a healthy and safe working environment. They can trigger ventilation systems to maintain optimal air quality.
What are the installation, maintenance, and lifecycle costs associated with smart lighting systems?
Understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) of smart lighting systems is crucial for budget planning.
While the initial installation can be higher due to specialized equipment and sensors, advancements in wireless technology and plug-and-play components reduce labor and wiring costs.
Smart lighting systems typically have lower maintenance costs. Automated monitoring and diagnostics detect issues early, reducing the need for routine inspections. LED technology, commonly used in smart lighting, has a longer lifespan and lower failure rates, further decreasing maintenance expenses.
Smart lighting offers significant cost savings over the system's lifecycle. Energy-efficient LEDs consume less power and last longer, reducing energy bills and replacement costs. The precise control of lighting levels and schedules minimizes energy waste, contributing to long-term savings.
Though initial costs may be higher, the extended lifespan of LEDs—up to 50,000 hours—means replacements are less frequent. When needed, the modular nature of smart lighting systems allows for easy component swaps without extensive rewiring.
Smart lighting systems also provide operational savings by reducing energy consumption, optimizing lighting based on real-time data, and minimizing downtime through predictive maintenance. These savings can offset the higher upfront costs over time, making the investment financially viable.
How can data analytics be leveraged to optimize lighting performance and maintenance schedules?
Data analytics enhances smart lighting systems by:
- Predictive maintenance - Analyzing data to predict and address potential failures before they occur, reducing downtime and extending system lifespan.
- Usage optimization - Adjusting lighting in real-time based on occupancy and daylight levels, ensuring optimal energy use.
- Performance monitoring - Tracking system performance to identify inefficiencies and improve lighting quality and energy efficiency.
- Energy consumption analysis - Identifying patterns and opportunities for energy savings through detailed consumption insights.
- Automated reporting - Generating reports with actionable insights on energy savings, system health, and maintenance needs for informed decision-making.
- Adaptive lighting controls - Automatically adjust
- lighting based on real-time data, ensuring appropriate lighting levels for different conditions.
What cybersecurity measures are in place to protect the smart lighting network?
Ensuring the security of smart lighting networks from cyber threats is critical for maintaining industrial operations. Key cybersecurity measures include:
- Encryption - Data transmitted between devices and control systems is encrypted to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity.
- Authentication and authorization - Strong authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), ensure that only authorized personnel can access the system. Role-based access control (RBAC) limits access to sensitive areas of the network.
- Network segmentation - Separating the smart lighting network from other critical industrial networks reduces the risk of widespread disruption in case of a cyber attack. This segmentation limits the potential impact of a breach.
- Regular software updates - Keeping firmware and software up to date protects against known vulnerabilities. Regular updates ensure the latest security patches are applied.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) - These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and potential threats, enabling timely detection and response to cyber incidents.
- Firewalls and secure gateways - Implementing firewalls and secure gateways helps block unauthorized access and control incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules.
- Data integrity checks - Regular integrity checks ensure that data has not been tampered with, maintaining the reliability of system operations.
- Security audits and penetration testing - Regular security audits and penetration testing identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the network, allowing for proactive remediation measures.
How scalable is the smart lighting solution for future expansions or modifications?
Smart lighting solutions are highly scalable and designed to adapt to future expansions or modifications with ease.
Their modular design allows components to be easily added or replaced without extensive rewiring, providing flexibility for straightforward upgrades and expansions.
Wireless communication protocols, such as Zigbee or Bluetooth, enable seamless integration of new devices without additional cabling, simplifying the process of expanding the system. This wireless capability ensures that new fixtures or sensors can be effortlessly incorporated into the existing network.
Cloud-based management platforms further enhance scalability by allowing centralized control and monitoring. These platforms make it easy to incorporate new features or adjust settings remotely, ensuring the lighting system can grow and adapt to meet changing needs. This flexibility makes smart lighting systems a viable long-term investment for any facility.
What is the impact of smart lighting on worker productivity and comfort?
Smart lighting significantly enhances worker productivity and comfort by creating environments tailored to human needs.
Adjustable lighting levels and color temperatures can mimic natural light, reducing eye strain and fatigue. This adaptability helps maintain circadian rhythms, improving sleep quality and overall well-being.
Dynamic lighting systems can adjust throughout the day to provide optimal lighting conditions for different tasks. Brighter, cooler light can boost concentration and alertness during the day, while warmer light can promote relaxation and reduce stress in the evening. This tailored approach supports mental and physical health, increasing productivity and job satisfaction.
Smart lighting can also enhance comfort by providing personalized lighting settings. Employees can adjust their workstation lighting to their preferences, improving comfort and reducing discomfort caused by inadequate lighting.
What environmental and sustainability benefits does the smart lighting system offer?
Smart lighting systems offer several environmental and sustainability benefits, including:
- Energy efficiency - Smart lighting systems use LED technology and automated controls to reduce energy consumption by adjusting lighting based on occupancy and natural light levels.
- Reduced carbon footprint - Lower energy usage translates to reduced carbon emissions, helping to decrease a building's overall carbon footprint.
- Compliance with environmental regulations - Smart lighting systems can help buildings comply with environmental regulations and standards, such as LEED certification, by optimizing energy use and reducing waste.
- Extended lifespan of lighting fixtures - LED lights used in smart lighting systems have a longer lifespan than traditional lighting, reducing the frequency of replacements and the associated environmental impact of manufacturing and disposing of bulbs.
- Minimized light pollution - Smart lighting can be programmed to reduce light levels or turn off lights when unnecessary, minimizing light pollution and its environmental impact.
- Resource conservation - Smart lighting systems conserve resources and reduce waste by using energy more efficiently and reducing the need for frequent replacements, contributing to more sustainable building practices.
Get the Full Story from EnOcean’s Whitepaper
For more information on smart building technology and IoT lighting, read EnOcean’s Whitepaper: Smart Buildings: IoT Solutions for Smart, Energy-Efficient Buildings.
To maintain the performance and longevity of LED lighting investments, proper surge protection needs to be a top priority.
Unfortunately, electrical surges caused by lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations can damage sensitive components, leading to costly repairs.
Surge voltage limiters act as the first defense, clamping high voltages to safe levels and protecting LED drivers and electronics. Surge limiter resistors manage the initial inrush current when the system powers on, ensuring smooth startup without damage.
Together, these devices enhance the reliability and lifespan of LED lighting installations.
Below, we’ll explore the functions of surge voltage limiters and surge limiter resistors, their integration into LED lighting systems, and best practices for designers and installers.
Understanding and implementing effective surge protection measures can help ensure consistent performance and reduce maintenance costs!
Understanding Surge Protectors and their Components
Proper surge protection in LED lighting systems involves various components that work together to prevent damage from electrical surges. Surge voltage limiters and surge limiter resistors play pivotal roles.
Surge Voltage Limiters
Surge voltage limiters are critical components designed to protect electrical equipment, including LED lighting systems, from transient overvoltages caused by events such as lightning strikes or power grid switching. These devices limit the voltage that can pass through the circuit, clamping it to a safe level that prevents damage to sensitive components.
In LED lighting systems, surge voltage limiters play a crucial role in maintaining system integrity and performance. LED drivers and other electronic components within the system are particularly susceptible to damage from voltage spikes.
By limiting the maximum voltage that can reach these components, surge voltage limiters help to extend the lifespan of the LED lighting system, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure consistent operation.
Surge Limiter Resistors
Surge limiter resistors are another vital component in the protection scheme of LED lighting systems.
These resistors are used in switching power supplies to limit the inrush current that occurs when the power supply is first energized. Inrush current can be significantly higher than the normal operating current, potentially damaging the power supply and connected components.
Surge limiter resistors help manage this initial surge, ensuring a smooth and safe power supply startup.
How Surge Voltage Limiters and Surge Limiter Resistors Integrate with Other Components
Surge voltage limiters and surge limiter resistors work in tandem with other protective components to form a comprehensive surge protection strategy.
In a typical LED lighting system, these components are integrated into the power supply circuit and the LED driver circuitry. The surge voltage limiter is the first line of defense, clamping high-voltage transients. The surge limiter resistor then manages the inrush current to prevent damage during power-up.
Together, these components ensure that the LED lighting system is protected from both instantaneous high-voltage spikes and prolonged overcurrent conditions. Proper integration of these elements safeguards the system and enhances its overall reliability and performance.
Best Practices for Lighting Designers and Installers
Incorporating surge protectors into LED lighting designs requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and compliance with industry standards.
Here’s what lighting designers and installers should know.
Design Considerations
Early integration - Surge protection should be considered early in the design phase of LED lighting systems. Integrating surge protectors from the outset ensures they are an integral part of the system rather than an afterthought.
Strategic placement - Position surge protectors close to the LED drivers or power supplies to maximize effectiveness. This minimizes the length of unprotected wiring and reduces the risk of voltage spikes reaching sensitive components.
Layered protection - Implement a multi-layered surge protection strategy by using different types of protectors at various points in the electrical system. This can include primary protectors at the service entrance and secondary protectors at the point of use.
System compatibility - Ensure that the surge protectors are compatible with all components of the LED lighting system, including drivers, controllers, and fixtures. Compatibility ensures seamless integration and effective protection.
Product Selection
Assess system requirements - Evaluate the specific needs of your LED lighting system, such as voltage levels, power capacity, and environmental conditions. This assessment helps in selecting surge protectors that meet these requirements.
Consider surge capacity - Choose surge protectors with an appropriate surge capacity rating. Higher surge capacity protectors can handle larger spikes, offering better protection for critical components.
Look for certifications - Select surge protectors tested and certified by reputable organizations. Certifications ensure that the products meet industry standards for safety and performance.
Check for additional features - Modern surge protectors often come with additional features such as diagnostic indicators, remote monitoring capabilities, and replaceable modules. These features can enhance the functionality and ease of maintenance.
Compliance and Standards
IEC Standards - The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides global standards for surge protection devices (SPDs), including IEC 61643, which outlines performance requirements and testing procedures.
UL Standards - Underwriters Laboratories (UL) offers several standards for surge protectors, such as UL 1449, which specifies safety and performance criteria for transient voltage surge suppressors.
IEEE Standards - The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) sets standards for surge protection in electrical and electronic systems, including IEEE C62.41, which provides guidelines for surge environment and protection.
National Electrical Code (NEC) - Adherence to the NEC ensures compliance with national safety standards for electrical installations. Surge protection requirements are outlined in Article 285 of the NEC.
Local regulations - Always check for local building codes and regulations that may have specific requirements for surge protection in lighting systems. Compliance with local codes is essential for safety and legal adherence.
Remember: surge protection devices aren’t foolproof. Sometimes, the protection isn’t strong enough for stronger lightning storms. For example, a lightning strike in Ottawa knocked out the LRT power lines despite having installed surge protection.
Protect Your Investments With Surge Protectors
LED setups and design elements are investments — you wouldn’t want to lose them to a sudden surge of lightning!
If your LED luminaires are unprotected, be sure to install surge protectors as soon as possible. It’s not 100% protection, but it’ll help you rest assured that your investments have the best possible safeguards against the elements.
How Architectural Lighting Transforms Brand Perception
June 6th 2024How Architectural Lighting Transforms Brand Perception
Branding has come a long way from its origins in simple signage, logos, and company colors.
It’s all about creating an experience that envelops customers, inviting them into a story filled with unforgettable visuals. This shift toward immersive brand experiences marks an evolution in how companies connect with their audiences, leveraging emotion and environment to leave lasting impressions.
Architectural lighting is at the heart of this approach — a strategic tool for mood setting and storytelling. The success of these sophisticated lighting designs depends largely on the power behind them: architectural LED power supplies.
These components are crucial in bringing the most innovative and technology-driven branding visions to life, ensuring that every detail works together to convey the brand’s message.
The Shift in Branding: From Signs to Sensations
Branding is no longer confined to the visual identifiers we’ve traditionally relied upon. It has expanded into a more holistic approach that embraces the full spectrum of sensory experiences.
This evolution shows how different sensory elements evoke emotions and create stronger consumer connections. From the texture of materials to the ambient sounds that fill a space, every detail helps reinforce the brand's story.
Interior design plays a pivotal role in this sensory branding. By thoughtfully designing spaces, brands can create immersive environments that do more than showcase their identity — they make it a lived experience.
These environments use color, light, and form in ways that go beyond aesthetics, actively contributing to the brand’s narrative.
Architectural lighting is critical in this setting. It shapes the space’s mood and directs attention, transforming ordinary rooms into scenes that capture the essence of the brand’s message.
Whether it’s the warmth of a dimly lit cafe that invites intimacy or the vibrant lights of a retail display that energizes shoppers, lighting is a powerful storyteller in the hands of today’s brands.
The Importance of Architectural Lighting in Brand Settings
Lighting does much more than illuminate a space. It shapes how we feel, perceive, and behave within that space.
In the context of branding, the strategic use of lighting can transform a branded space into an aesthetic setting that communicates and reinforces the core attributes of the brand.
By influencing mood and perception, lighting becomes a dynamic tool in creating an unforgettable brand experience that can elicit specific behavioral responses, such as increased dwell time in stores or enhanced feelings of comfort in hospitality settings.
Various lighting strategies play distinct roles in enhancing brand identity.
- Colored lighting, for example, can evoke different emotions — blue tones might convey a sense of tranquility, while red might energize and excite.
- Color temperature is also important, depending on the space you want to create. Warm lighting can relax, while cool lighting is best for high visibility.
- Spotlights can highlight key products or architectural features, drawing attention strategically and creating focal points that guide the customer journey.
- Uplighting, on the other hand, adds drama and dimension to a space, enhancing architectural details and creating an uplifting ambiance.
Each of these lighting techniques can be meticulously integrated to support the brand’s narrative, ensuring that the lighting serves functional purposes and contributes to a memorable brand experience.
Architectural LED Power Supplies: The Unsung Heroes
While the visible elements of architectural lighting capture our immediate attention, the true enabler of these innovative designs is behind the scenes: the architectural LED power supplies.
LED drivers transform creative concepts into tangible experiences that users can consistently enjoy. They ensure lighting installations' longevity and reliability while enhancing their efficiency and adaptability to different settings.
Technical considerations are key to understanding why these power supplies are so essential.
- They provide steady and controlled power to LED fixtures, crucial for maintaining the quality and consistency of lighting — factors that directly impact the perceived quality of the space and, by extension, the brand itself.
- LED power supplies are designed to be energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, aligning with global trends toward sustainability.
- This helps brands reduce operational costs and strengthens their commitment to eco-friendly practices, a growing concern among consumers.
The adaptability of LED power supplies in terms of dimming capabilities and integration with smart lighting systems also plays a role, allowing for dynamic lighting scenarios.
In the realm of architectural lighting, Bluetooth technology has emerged as a pivotal tool for controlling LED systems. It empowers lighting designers to fine-tune numerous lighting performance parameters, ultimately transforming the aesthetic and functionality of a space.
This adaptability is essential in today's market, where the ability to adjust lighting based on time of day, event type, or desired ambiance can significantly enhance the user experience and further embed the brand's identity within the minds of its customers.
Architectural LED power supplies are not just supporting players but central figures in the narrative of modern, effective branding through lighting.
Examples of Lighting Elevating Brand Experience
Having worked with many brands over the years, GRE Alpha has many examples of how lighting can take brand experience to the next level.
Here are a few examples.
Hotel Janu, Azabudai Hills, Tokyo
The lobby of Janu Tokyo, a flagship of Aman Resorts' new luxury brand, is a prime example of how lighting can become a crucial element of the brand experience through simple illumination.
Using GRE Alpha's GLD-DIM-DMX4I-L smart lighting control modules, the hotel achieves a blend of Japanese minimalism and European elegance. These DMX modules create color-changing scenes that accentuate high-arched ceilings and the interplay of natural and sophisticated design elements.
This lighting strategy highlights the lobby's architectural beauty and creates a warm, welcoming atmosphere that transforms the hotel entrance into a luxurious experience, deeply resonating with the brand’s understated luxury.
Andaz Xintiandi, Shanghai
In the heart of Shanghai's Xintiandi district, Andaz Xintiandi uses architectural lighting to enhance its environment and support the brand's philosophy of personalized guest experiences.
The hotel is equipped with GRE Alpha’s SLD and XLD smart dimming modules, critical for creating a subdued, comfortable ambiance that mirrors the glamorous 1920s Shanghai nightlife.
This lighting setup complements the hotel's luxurious and futuristic design and plays an integral role in energy optimization and glare control. By maintaining low brightness levels with balanced control, the lighting at Andaz Xintiandi ensures a refined comfort that aligns with the wellness and wellbeing themes central to the brand.
Louis Vuitton Storefront Facades
Louis Vuitton, a global luxury brand known for its high-end fashion products, uses lighting as a strategic tool to enhance its storefront facades, creating a visually stunning experience that attracts and captivates customers.
Employing GRE Alpha’s SLD-DIM1X dimming module, the brand achieves ultra-high-resolution dimming, which is essential for the smooth, flicker-free display of its outdoor LED signage.
This technology allows for nuanced control of lighting, from bright to very dim, enhancing the visual appeal of the stores and reinforcing the brand's image of luxury and exclusivity.
The effectiveness of Louis Vuitton's lighting techniques not only highlights the brand’s creative flair but also supports its reputation as a purveyor of desirable and luxurious goods.
Designing with Light: Tips for Brands Looking to Innovate
Elevating brand experience with LED lighting starts with a plan. Here are some tips to get started.
1. Start with a Vision
Before diving into specifics, brand managers should clearly define what they want to achieve with their lighting.
Whether setting a mood, highlighting products, or creating an immersive environment, the objectives should guide the lighting design from the outset. This will help them determine what elements to include—different colors, color temperatures, dimming features, and more.
2. Involve Experts Early
Incorporate lighting designers and technical experts early in the planning process.
These professionals can provide valuable insights into the latest technologies and how they can be applied to achieve your branding goals. Their expertise will be crucial in turning conceptual ideas into feasible, impactful designs.
3. Choose the Right Technology
Selecting the right LED power supplies and lighting technology is critical.
Consider LED driver factors such as energy efficiency, color rendering index (CRI), and dimming capabilities. For instance, GRE Alpha’s modular power supplies offer flexibility and can be tailored to meet specific needs, ensuring both functionality and sustainability.
4. Experiment with Controls
Use smart lighting controls to adjust the ambiance and react to different scenarios or times of day.
Programmable settings can instantly transform a space and allow for dynamic interactions with the environment, making the lighting setup functional and an active participant in the brand story.
5. Ensure Consistency Across Touchpoints
Consistency in lighting across all brand touchpoints reinforces brand recognition and enhances customer experience.
Ensure that the lighting is uniform in quality and intensity, whether in-store, in an office, or during an event.
6. Prioritize Collaboration
Encourage ongoing collaboration between brand managers, designers, and technical experts.
This synergy is essential for ensuring that the lighting is aesthetically pleasing and aligns perfectly with the brand’s values and message. Regular reviews and adjustments based on feedback can lead to a more refined and effective lighting strategy.
7. Test and Iterate
Finally, testing different lighting setups and gathering feedback is vital.
What works in one setting might not work in another, and customer perceptions can provide critical insights that drive better decisions. Iterative testing and refinement will help pinpoint the most effective solutions for engaging customers and enhancing the brand experience.
The Future of Branding and Architectural Lighting
As we look toward the future, the role of architectural lighting in branding is poised for even more transformative shifts, driven by advances in technology and changing consumer expectations.
Here’s what we can anticipate in the realms of architectural lighting and how these trends may revolutionize branding strategies:
1. Integration of IoT and Smart Technology
The Internet of Things (IoT) integrates with architectural lighting in real time, allowing brands to engage with consumers in ways that enhance the overall experience.
Smart lighting systems that adjust based on environmental changes or user interactions will provide brands with dynamic tools to enhance customer experience.
For instance, lighting that changes color or intensity based on the time of day or the number of people in a space could become common, making environments more responsive and immersive.
2. Human-Centric Lighting
As understanding of the impact of light on human health and behavior grows, expect to see more human-centric lighting solutions that enhance well-being.
This approach tailors lighting to support natural circadian rhythms, potentially boosting mood and productivity. Brands focusing on well-being could use these technologies to strengthen their market position and connect more deeply with their customers’ lifestyles.
3. Advances in LED Technology
LED technology will continue to evolve, becoming even more energy-efficient and capable of producing a wider spectrum of light qualities.
Developments in LED power supplies will likely focus on enhancing the color accuracy and the smoothness of dimming features, which are critical for creating atmospheres that precisely match a brand’s desired aesthetic and functional needs.
4. Sustainable Lighting Solutions
Sustainability will remain a major theme, with innovations aimed at reducing the environmental impact of lighting solutions.
Future LED power supplies may incorporate materials that are easier to recycle or consume less energy, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and helping brands solidify their commitment to sustainability.
5. Customization and Personalization
We will see an increase in customizable and personalized lighting options, where consumers can alter the lighting to suit their preferences or activities via apps or voice commands.
This shift will empower users to interact with brand spaces in more personal ways, potentially increasing engagement and loyalty.
6. Virtual and Augmented Reality Experiences
Augmented and virtual reality technologies could be integrated with architectural lighting to create layered, multisensory brand experiences.
For example, lighting could be used to enhance virtual product demonstrations or to create immersive environments that blend physical and digital elements.
Learn More About GRE Alpha’s Role Using Lighting to Elevate Brands
As a consistent innovator in the LED lighting industry, GRE Alpha continues to create solutions that help brands stand out with their lighting design.
From LED drivers to dimming technology, we have solutions for all different scenarios. Learn more about our technology today.
Wireless Lighting Controls: A Total Cost Analysis
May 9th 2024Wireless Lighting Controls: A Total Cost Analysis
As lighting tech continues to advance, so does the opportunity for additional cost savings — particularly when it comes to wireless lighting controls.
Our partner, EnOcean, published a whitepaper covering important insights and analyzing the cost implications of implementing wireless lighting controls. Here are some of the key points.
Concerns and Opportunities for Building Owners
Building owners are constantly pressured to manage costs while enhancing building functionality and sustainability.
With rising electricity rates and increasing demands for energy efficiency, wireless lighting controls are a strategic solution that aligns with economic and environmental goals. These systems are pivotal in reducing reliance on costly energy sources and minimizing greenhouse emissions.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
Wireless lighting controls significantly reduce electricity consumption by optimizing lighting usage through advanced technologies such as occupancy sensors, daylight harvesting, and personal control settings.
Studies indicate that lighting accounts for a substantial portion of energy used in buildings, with a considerable percentage being wasteful. By integrating intelligent lighting controls, buildings can save between $0.60 to $1.00 per square foot in energy costs.
Flexibility and Enhanced Productivity
Wireless controls offer unmatched flexibility, allowing for easy installation and reconfiguration without disrupting conventional wiring methods.
This adaptability extends to controlling individual lights, groups, or entire building systems from a centralized or remote location. Research also highlights that proper lighting improves workplace productivity and employee satisfaction, further justifying the investment in these modern systems.

Imagine a design that boosts productivity and satisfaction with simple controls
Wireless Systems for Long-term Value
Wireless and smart lighting control systems outperform wired ones in certain retrofit scenarios due to lower installation costs and minimal structural disruption.
While the initial material cost for wireless systems might be higher, the overall expenditure, when factored with installation labor and future flexibility, positions wireless as a more cost-effective solution over time.
Energy Harvesting: A Sustainable Future
A pivotal advantage of modern wireless lighting controls is their ability to operate without batteries, utilizing energy harvesting technologies. This innovation captures energy from environmental sources like solar, kinetic, or thermal energy, reducing dependency on batteries and their associated maintenance and disposal costs.
Specific Use Cases
Wireless lighting controls can see usage across many different industries and in several use cases. Here are some examples:
- Office space - Wireless sensors can help building managers optimize lighting usage in offices and eliminate any unnecessary costs.
- Restrooms - With wireless sensors, building managers can better understand how often restrooms are used to optimize maintenance and keep customers happy.
- Hotel and campus projects - Despite these facilities often being unoccupied, appliances that use energy are often left on — including lighting. Wireless sensors can switch these appliances off to conserve energy.
- Assisted living projects - As healthcare facilities become more expensive and less available, wireless occupancy sensors can help reduce costs in different ways, such as turning off lights when rooms are empty.
Use Cases
EnOcean also published fact sheets to dive into specific benefits by project type. Here’s a quick summary of a few of them:
- Open Office Area - Installing wireless sensors and controls in an office environment demonstrated a payback period of just 2.3 years, with a 41% cost saving over wired alternatives.
- Classrooms - In educational settings, where lighting controls included occupancy sensors and daylighting, the technology achieved a payback period of 3.3 years, offering a 39% savings compared to wired systems.
- Warehouses - For industrial spaces, wireless controls centered around occupancy sensors delivered a payback in less than a year (0.8 years), emphasizing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of wireless solutions in large, energy-intensive environments.
Read the Full Whitepaper From EnOcean
To learn more about the wireless lighting controls cost and dive into the details, you can read the whitepaper from EnOcean here.
As a valued partner, GRE Alpha also carries a wireless dimming module compatible with EnOcean switches. You can find more information on the ENO-DIM dimming module here.